Sen. Loren Legarda proposed the creation of the Philippine Space Agency, which will address the country's issues related to space science and technology applications. The senator filed Senate Bill 1259 or "An act establishing a Philippine Space Development Policy and creating the Philippine Space Agency (PhilSA), […] It must be considered that the Philippines is lagging behind its neighbouring countries, such as Indonesia, Malaysia, Vietnam and Singapore, each having Space Agencies with satellites devoted on telecommunications or earth monitoring - Manila Star, 3rd January 2017 A big welcome from the Team at InnovaSpace to this our first Space Blog. We are a new Space Consultancy bringing a huge wealth of experience through our team members and Board of Advisors, all of whom have long and notable careers within their fields. Space is a subject that has personally inspired many of them, together with generations of people all over the world who have looked up to the stars with curiosity.
The distance between Space Science, Space Discovery and society at large has progressively narrowed since the late 1950s and 60s - a period in which Russia launched Sputnik 1, NASA developed Project Mercury, Yuri Gagarin became the first man in space, Alan Shephard Jr the second, and Valentina Tereshkova the first woman. Today, Space is no longer in the hands of the few: now Space occupies the mind of almost every national government, aware of the need for greater inclusion, participation, knowledge transfer and professionalization in this universal project. We no longer speak of simply the Moon as we once did, but of Mars and humanity's eventual off-world migration - as there were Neil Armstrong's first steps, so too will there be humanity's fledgling movements on Mars, facilitated by the maturity and sophistication of mechanics, engineering, physiology and astrophysics. Human spaceflight has, furthermore, become no longer the province of one nation, but the intention of many: China has been added to the list of nations to send a manned spaceflight into orbit, with the launch in 2003 of taikonaut Yang Liwei on board the Shenzhou 5 spacecraft. There are now three nations with human spaceflight and lunar soft-landing capability: the USA (NASA), Russia (Roscosmos) and China (CNSA). However, it should not stop here: with Space on the developmental agenda for many emerged and emerging nations, participation and opportunity will define Space not only as a critical research area for the advancement of the sciences, but as a platform for national progress, social development and regional leadership. At the governmental level, many new space agencies have been formed, some with launch capabilities, such as the European Space Agency (ESA), Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). The globe is in fact home to a total of 65 space agencies, as seen in the maps below, and these vary in budget, size, operational capability and potential, the majority of which are concentrated in Europe. Space science technology is often considered a luxury only for developed countries, but it’s actually a basic and vital need for development [...] - Solomon Belay, director of the Entoto Observatory and Research Centre. What we do and why we do itThe National Academy of Medicine of Mexico, aware of the importance of the subject, enthusiastically adhered to the project initiated by the Mexican Space Agency in order to strengthen the Mexican space medicine program. The main objective of the program is to promote the development of scientific and technological research in space medicine. As with the increased importance of the Space Sciences for the fields of medicine, technology and engineering, so too have the demands for practical developments in these areas increased globally. Ownership of these sciences is global and diverse, yet the way in which they are strategically facilitated, scientifically cultivated and globally marshalled will determine the successful growth of a nation's rate of participation in Space.
InnovaSpace is the consequence of (1) this modern need for increased participation in Space through the international development of the Space Sciences and, (2) the model established from the successful development and evolution of an inter-disciplinary centre in the Space Sciences, the MicroG, created at the Pontifical University of Rio Grande do Sul (PUCRS) through the initiative of InnovaSpace Founder, Professor Thais Russomano.
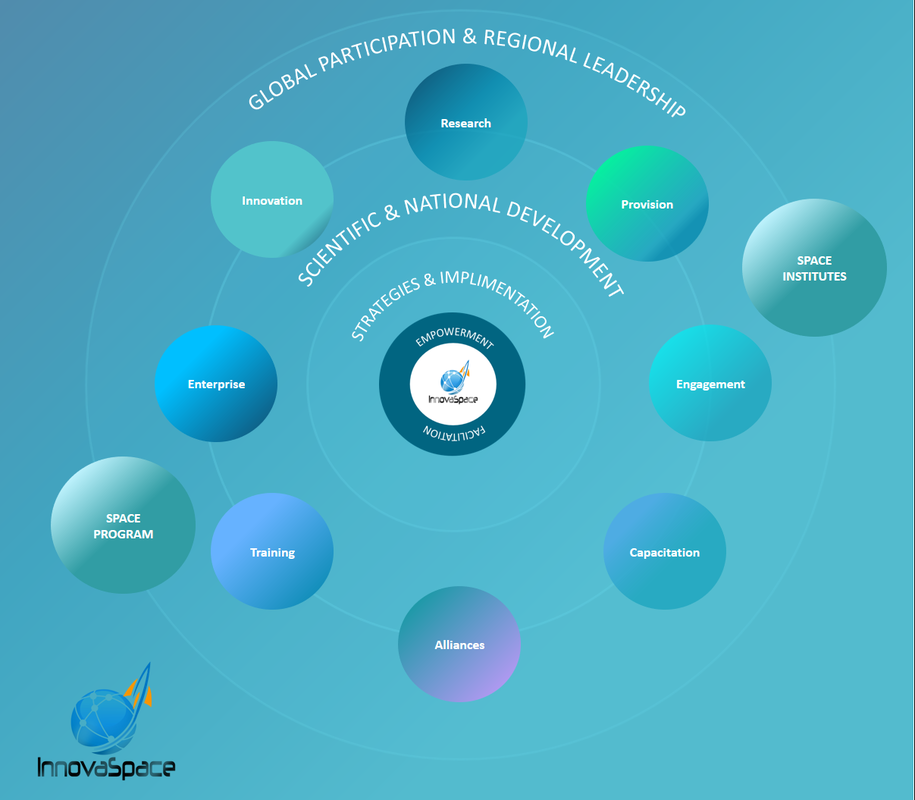
The maps above show the global pattern of space agencies, yet this does not necessarily imply that all countries, especially those in Latin America, Africa and the ASEAN have developed the programs, training, pathways and direction necessary to cultivate and harness domestic talent to effectively participate in Space. Innovaspace brings the collective scientific strengths and experience of its advisory board, as well as its global network of scientists, clinicians and engineers together, in order to provide scaled solutions across a variety of areas crucial for the successful cultivation and growth of national space programs. Innovaspace Engagement Model Innovaspace works across three distinct phases of engagement: (1) Strategies & Implementation; (2) Scientific & National Development and, (3) Global Participation & Regional Leadership. Across these three phases, expertise are deployed to empower and facilitate eight areas necessary for effective Space Programs and fully-functioning Space Science Institutes (SSIs). Not all nations, however, will have the same needs: there will be those requiring the introduction of research programs that enable expertise in the space life sciences; others, will be ready to combine institutes and talent into a specialist centre, much like the MicroG in Brazil, with the use of specific technology, equipment, ideas and personnel. In either case, the cultivation of an international space network (Alliances) channelling national and regional research and innovation expertise across the globe is a reality that Innovaspace equally desires, to define national and global progress in Space Science. Innovaspace seeks to empower, enable and facilitate the development of space science centres and programs that will drive global participation and regional leadership in a time when Space has become an integral part of national scientific policy and an instrument for development. We look forward to the challenge of helping nations advance their Space participation, from a grassroots level of facilitating public access to Space knowledge, through to governmental levels in building scientific platforms to promote national progress and social development. Ad astra and let the work commence. Comments are closed.
|
Welcometo the InnovaSpace Knowledge Station Categories
All
|
InnovaSpace Ltd - Registered in England & Wales - No. 11323249
UK Office: 88 Tideslea Path, London, SE280LZ
Privacy Policy I Terms & Conditions
© 2024 InnovaSpace, All Rights Reserved
UK Office: 88 Tideslea Path, London, SE280LZ
Privacy Policy I Terms & Conditions
© 2024 InnovaSpace, All Rights Reserved
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed